Inflammation
Summary
Inflammation is a response by the immune system that eliminates threats in the body. When the threat is not removed it becomes chronic and can initiate cancer. [1-7] As seen in Figure 1, when inflammation occurs, the area of inflammation is flooded with red blood cells that recruit nutrients and immune cells, which keep infections from spreading. Imagine the inflammatory response as a fire and the blood cells as fire fighters. If there was a fire and the fire fighters arrived at the scene quickly it would lead to the quick containment of the fire. This scenario depicts a normal inflammatory response. However, if the fire grew it would become harder and harder to contain. This would make the response chronic. [1,2]
Chronic inflammation can lead to heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and cancer. Inflammation can help to initiate cancer development in several ways. For instance, during chronic inflammation potent microbial agents are released to directly target threats. However, this can lead to DNA damage, which can cause mutations leading to cancer initiation. Likewise, inflammation promotes new blood vessel formation, causing rapid cancer cell reproduction, tendency to spread, and making it difficult to fight off infections. [2] This generates the perfect environment for cancer growth and development.

Arizbeth Lopez
Undergraduate from Lamar University
There are some supplements that have the potential to reduce chronic inflammation in the body. For instance, beta glucans, sugars found in bacterial and fungal cell walls, are supplements that have compiled substantial research that regarding their ability to reduce inflammation. [3] There are other supplements, such as organic germanium, which are claimed to possess anti-inflammatory properties. However, it is only safe in trace amounts normally found in the diet and is deemed likely unsafe when taken in its elemental form and in certain compounds. Overuse can lead to kidney failure, damage to other organs, anemia, muscle weakness, and nerve problems, among many other side effects. [8] This is why it is important to research any theories and therapies in healthcare and consult a physician before implementation.
So, what causes inflammation? As seen on Table 1, inflammation is primarily caused by physical and biological factors. [4,5] Physical factors include radiation as well as chemical factors. Biological factors are things such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi which cause inflammation through infection, and can also cause cell DNA damage. When infection is detected in the body, the immune system can activate the inflammatory response to fight off the infection. Additionally, obesity can also be linked to several types of cancer. This happens due to the over accumulation of nutrients. When cells store nutrients for a long period of time, they begin to release toxins which will activate the inflammatory response as well as cause cell damage. [5]
In reality, there is not one cause of cancer. Cancer can come about due to a combination of factors. Therefore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is one of the most crucial steps to take for cancer prevention.
References
- Pahwa R, Goyal A, Bansal P, Jialal I. Chronic Inflammation. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020.
- Aguilar-Cazares D, Chavez-Dominguez R, Carlos-Reyes A, Lopez-Camarillo C, Hernadez de la Cruz ON, Lopez-Gonzalez JS. Contribution of Angiogenesis to Inflammation and Cancer. Front Oncol. 2019; 9:1399. Published 2019 Dec 12. doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.01399
- Vetvicka V, Vannucci L, Sima P, Richter J. Beta Glucan: Supplement or Drug? From Laboratory to Clinical Trials. Molecules. 2019;24(7):1251. Published 2019 Mar 30. doi:10.3390/molecules24071251
- Qian S, Golubnitschaja O, Zhan X. Chronic inflammation: key player and biomarker-set to predict and prevent cancer development and progression based on individualized patient profiles. EPMA J. 2019;10(4):365-381. Published 2019 Nov 20. doi:10.1007/s13167-019-00194-
- Todoric J, Antonucci L, Karin M. Targeting Inflammation in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2016;9(12):895-905. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-16-0209
- Kompella P, Vasquez KM. Obesity and cancer: A mechanistic overview of metabolic changes in obesity that impact genetic instability. Mol Carcinog. 2019;58(9):1531-1550. doi:10.1002/mc.23048
- Basen-Engquist K, Chang M. Obesity and cancer risk: recent review and evidence. Curr Oncol Rep. 2011;13(1):71-76. doi:10.1007/s11912-010-0139-7
- Germanium: Health benefits, uses, side effects, dosage & interactions. Rxlist.com. https://www.rxlist.com/germanium/supplements.htm. Accessed August 4, 2020.
Full Article
Cancer is the uninhibited growth of abnormal cells in any location of the human body. This growth can be caused by a number of factors, including environmental components, carcinogens, mutations, infection, obesity and inflammation. Inflammation can be attributed to higher risk and prevalence of the disease. [1-6] While inflammation can sometimes be overlooked as a cause of cancer, it is estimated that 20% of cancers are associated with inflammation. [6] Inflammation can give cancerous cells the optimal environment to invade the natural mechanisms of an individual. [1] In order to see how inflammation provides this kind of environment for cancer cells, it will be useful to look at how the inflammatory response works.
Inflammation is a response by the immune system to a detected threat in the body. While it is intended to promote healing, when the threat is not destroyed it becomes chronic and can help initiate cancer growth. [2] During normal circumstances, the area of inflammation is flooded by blood. In the blood, there are red blood cells which bring nutrients to the affected area, and white blood cells, or immune cells, which work to keep infections from spreading. Let’s think of the inflammatory response as a fire and think of the blood cells as firefighters. Imagine that a fire starts in a forest and the firefighters are able to quickly localize the fire. This would lead to a quick containment of that fire with minimal damage. Likewise, when the inflammatory response is effective, the threat is stopped, and the inflammation will subside. As seen on Figure 1, in cases where the inflammatory response does not work effectively, the response continues to be stimulated and can cause chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation is the long-term response of the immune system which can last several months or years. [1] Think of this as if the firefighters were delayed to the scene and therefore the fire grew too large to be contained. Chronic inflammation can lead to heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and cancer.
While our understanding of inflammation dates to ancient times, it was not until 1828 that French surgeon and pathologist Jean Nicholas Marjolin was able to link inflammation to causing cancer. [2,4] He made this conclusion after observing cancerous growths developing around inflamed burn wounds on the uppermost layer of the skin. [4] This is because inflammation promotes some of the key hallmarks of cancer such as: cancer cell reproduction, creation of new blood vessels, tumor invasion, and even limits the effectiveness of anti-cancer drugs and treatments. [3]
How does this happen? Going back to our uncontained fire example, say that after the first group arrives, they realize they need backup, but the fire has become so big that the road is too dangerous to navigate. While the other fire departments are trying to find a way to get to the group that is containing the fire, they decide to cut through part of the forest that is not burning to get to them, essentially creating a new road to get help to the other firefighters. That is exactly the response that happens in the body when the inflammation becomes too extreme. Blood cells begin to replicate and migrate to form new blood vessels. These blood vessels aid in the transportation of more blood cells due to up regulation of the inflammatory response. Although the body does this as a way to heal itself from a threat, it can be harmful in several ways. During chronic inflammatory response, the immune system releases potent microbial agents that are meant to directly attack invaders in the body but can also cause cell damage. The damage can lead to mutations of the cell’s DNA which can trigger the development of cancer. Even if the mutations were not enough to initiate cancer growth the mutations could cause a release of pro-inflammatory factors which would further stimulate the inflammatory response, thus initiating cancer. Additionally, the creation of new blood vessels would inevitably lead to the perfect cancer microenvironment.
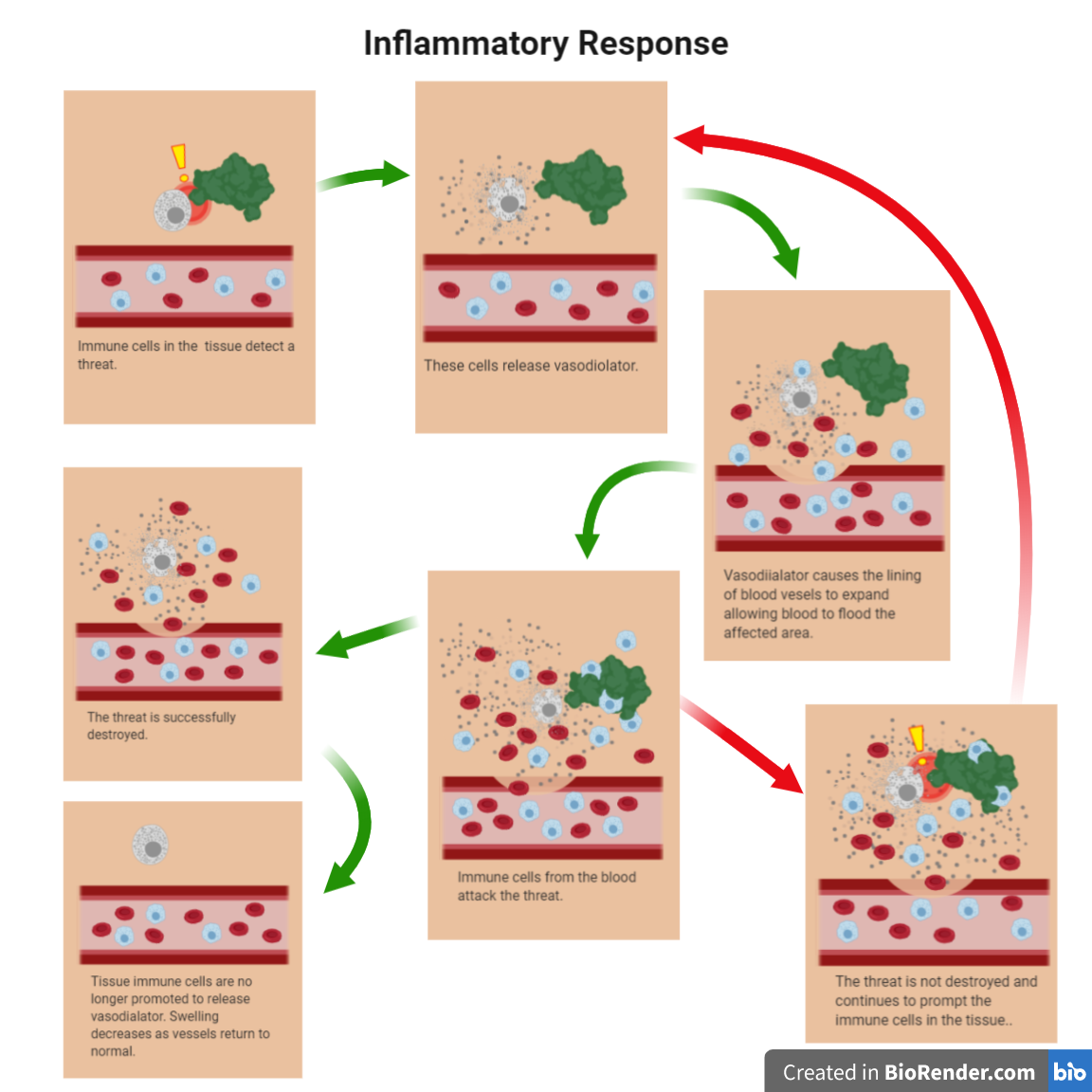
Figure 1: Inflammatory Response. This figure describes the different steps that take place during the inflammatory response. Acute inflammatory response (normal) is represented by green arrows, while chronic inflammatory response (abnormal) is represented by red arrows.
This means allowing rapid cell reproduction, promoting the tendency of cancer cells to spread, making it difficult for the body to fight off infection, and changing the metabolism of the cell in such a way that it promotes tumor development. In other words, the new blood vessels cause a domino effect which is beneficial to the development of cancer. [3]
So, what causes inflammation? As seen in Table 1, inflammation is primarily caused by physical external factors such as radiation, chemical factors like carcinogens, and by biological factors such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. [5]
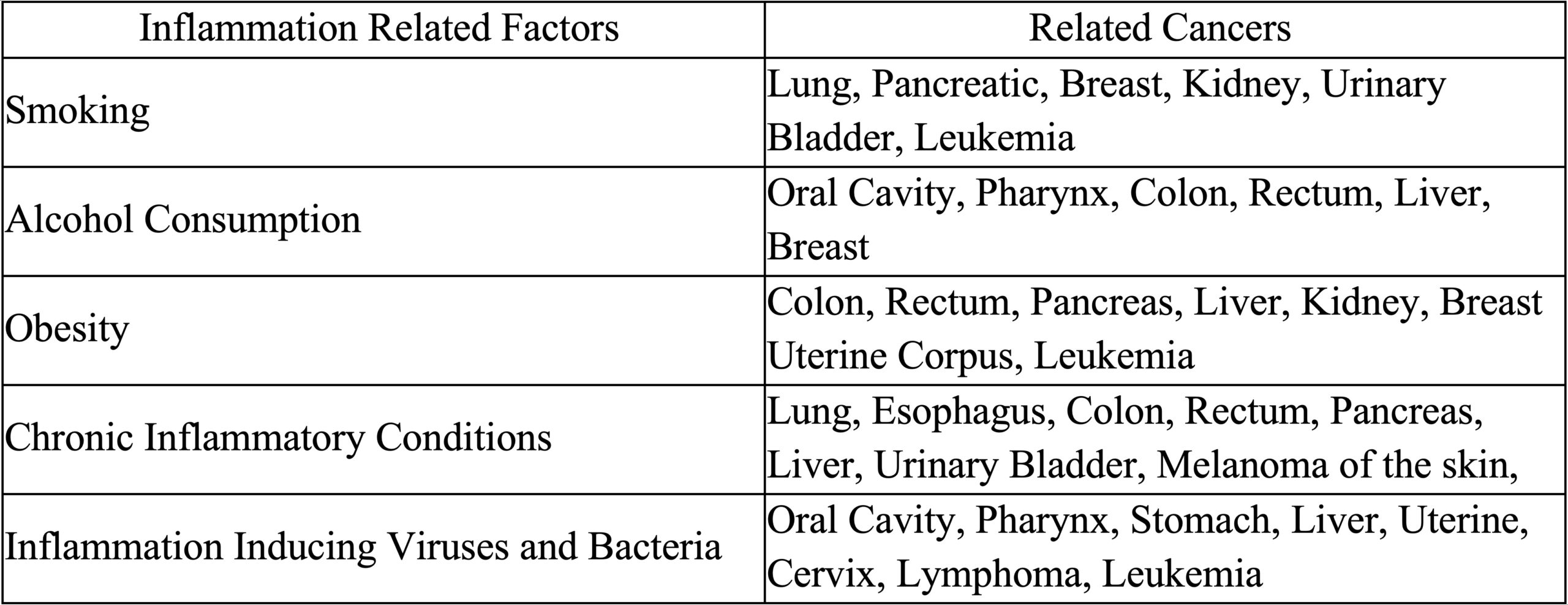
Table 1: Cancers Related to Inflammatory Factors. This table outlines the most prominent inflammatory factors and related cancers. [5, 6]
Each of the factors described in Table 1 lead to inflammation, which as discussed above can lead to the development of cancer. They do this in several ways, for example, cigarette smoke increases the risk of developing lung cancer due to entering chemicals, which cause inflammation to occur. Furthermore, the consumption of alcohol has been associated with higher risk of cancers such as neck, esophageal, breast, liver and pancreatic. This is because constant use of alcohol causes irritation, which causes an inflammatory response. [6] There is also adequate evidence which links obesity to several types of cancer including: colon, endometrial, kidney, and esophageal cancer. This happens due to the over accumulation of nutrients for a long period of time. By way of analogy, if you store food for too long it will go bad. Likewise, when cells store nutrients for a long period of time, they begin to release toxins which will activate the inflammatory response and as explained previously, if left untreated this can lead to chronic inflammation. [7,8] Lastly, viruses and bacteria are also correlated as a cause of cancer, such as lymphoma and leukemia among others. When an organ becomes infected with a virus or bacteria it can lead to inflammation. While inflammation does not automatically mean infection, an infection can cause inflammation. If you have a scrape or a cut and it gets infected chances are that wound will also be swollen. That same process can happen internally if something gets infected. The immune system will activate the inflammatory response to fight off the infection, and, if left untreated, the infection can lead to chronic inflammation.
The immune system also plays an important role in protecting us against cancer and tumor growth, therefore building a strong immune system can be favorable in cancer prevention. There are theories surrounding the use of supplements or drugs to help build the immune system. For instance, beta glucans are sugars found in bacterial and fungal cell walls. They are considered immunomodulators, which are substances that can interact with the immune system and stimulate or suppress parts of the immune response. [9] Beta glucans are immunostimulants, meaning they stimulate the immune response. Although it is an immunostimulant, it also can help reduce risk of cancer by reducing inflammation. [10] Additionally, studies show that beta glucans have strong activity against a variety of tumors. Although there are many clinical trials, the most successful are researching beta glucans in combination with lab engineered antibodies. Beta glucans have the ability to work alongside antibody therapy to promote tumor-killing mechanisms. However, trials are also showing that beta glucans have similar effects alone. The mechanism of action seems to be the use of antitumor antibodies which are naturally produced in the body. [9]
Likewise, inositol hexaphosphate (IP6), an active compound found in rice and other grains, is known for its anti-cancer properties. Several studies have proven that IP6 has preventative as well as therapeutic potential due to several factors, including immune-enhancement, and anti-inflammatory activities. IP6 also acts alongside cancer therapies to inhibit cancer hallmarks. Furthermore, in vitro (cellular) studies have shown that it promotes the termination of human breast cancer cells. [11]
Conversely to both beta glucans and IP6, organic germanium is a chemical element often erroneously thought to help with cancer prevention and progression. [10-12] Organic germanium has been researched in association with treatment for several types of cancer and has not shown any significant response. However, it can be used by the body to stimulate the immune system as well as reduce inflammation. Organic germanium is only safe in trace amounts normally found in your diet and is deemed likely unsafe when taken in its elemental form and in certain compounds. Overuse can lead to kidney failure, damage to other organs, anemia, muscle weakness, and nerve problems, among many other side effects. [12]
All things considered, it is important to do as well as understand the research behind potential theories and therapies in healthcare. For instance, if someone were to read a mistaken article that said that organic germanium is helpful for prevention of cancer and decided to start taking the supplement without doing proper research or consulting a physician, it could lead the person to developing one of the side effects previously mentioned.
In summary, inflammation is a major contributor to cancer development due to its ability to create the most favorable environment for cancer cells to grow. It is important to understand that if inflammation is left untreated it becomes chronic, and chronic inflammation is what sets the stage for cancer development. This scenario can occur when cells become damaged due to the release of microbial agents leading to mutation, and rapid cell reproduction, which are major cancer hallmarks. Additionally, the inflammatory response leads to the creation of new blood vessels that begins a domino effect, which leaves behind a cancer cell promoting environment. Inflammation can be caused by an injury or by physical factors such as radiation and chemicals, as well as biological factors which include bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The immune system is our most important method of protection against foreign invaders in the body, this includes cancer and tumors. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, so that our immune system can continue to keep us safe.
References
- Pahwa R, Goyal A, Bansal P, Jialal I. Chronic Inflammation. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020.
- Aguilar-Cazares D, Chavez-Dominguez R, Carlos-Reyes A, Lopez-Camarillo C, Hernadez de la Cruz ON, Lopez-Gonzalez JS. Contribution of Angiogenesis to Inflammation and Cancer. Front Oncol. 2019; 9:1399. Published 2019 Dec 12. doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.01399
- Vetvicka V, Vannucci L, Sima P, Richter J. Beta Glucan: Supplement or Drug? From Laboratory to Clinical Trials. Molecules. 2019;24(7):1251. Published 2019 Mar 30. doi:10.3390/molecules24071251
- Qian S, Golubnitschaja O, Zhan X. Chronic inflammation: key player and biomarker-set to predict and prevent cancer development and progression based on individualized patient profiles. EPMA J. 2019;10(4):365-381. Published 2019 Nov 20. doi:10.1007/s13167-019-00194-
- Todoric J, Antonucci L, Karin M. Targeting Inflammation in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2016;9(12):895-905. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-16-0209
- Kompella P, Vasquez KM. Obesity and cancer: A mechanistic overview of metabolic changes in obesity that impact genetic instability. Mol Carcinog. 2019;58(9):1531-1550. doi:10.1002/mc.23048
- Basen-Engquist K, Chang M. Obesity and cancer risk: recent review and evidence. Curr Oncol Rep. 2011;13(1):71-76. doi:10.1007/s11912-010-0139-7
- Germanium: Health benefits, uses, side effects, dosage & interactions. Rxlist.com. https://www.rxlist.com/germanium/supplements.htm. Accessed August 4, 2020.